
For example, some families had only daughters, and others had firstborn sons who were unsuitable for the duties of the heir. In some families, this worked out well – but in others, it posed major issues. This is often still the case in modern times. In European feudal systems, the firstborn son usually inherited the family land. In Japan, we tend to see a collectivist attitude – where citizens work as a community for the good of the country as a whole. In Europe, we tend to see individualistic societies – where each person strives towards their own personal goals. Interestingly, you can see the after-effects of these two separate ethos in Europe and Japan today.
This left very little room for revolt if the nobility were not serving their people well. The ethos of the Chinese system placed an emphasis on the unconditional loyalty of citizens to the nobility, regardless of their actions. In Japan’s feudal system, the relationship between nobility and citizens was modeled on the Chinese system. Should the nobility let down the citizens in feudal Europe, a revolution was a possibility. Under this ethos, loyalty to the nobility was conditional on the nobility fulfilling their side of the bargain – in other words, keeping citizens protected and providing reasonable living conditions. Legalistic vs Unconditional LoyaltyĮurope’s feudal system encouraged a legalistic style relationship between nobility and citizens, based on Roman law. Actually, if you take a look at modern Japan and Europe, you could easily pick out differences that directly correlate with how things were hundreds of years ago! 1. Naturally, Japan and Europe would have more differences than similarities. 5 Differences Between The Japanese Shogunate And Feudal Europe There were even pronounced physical similarities between the samurai and the knight class – both wore a suit of armor, and both rode horses.
#Europe and japan feudalism chart code#
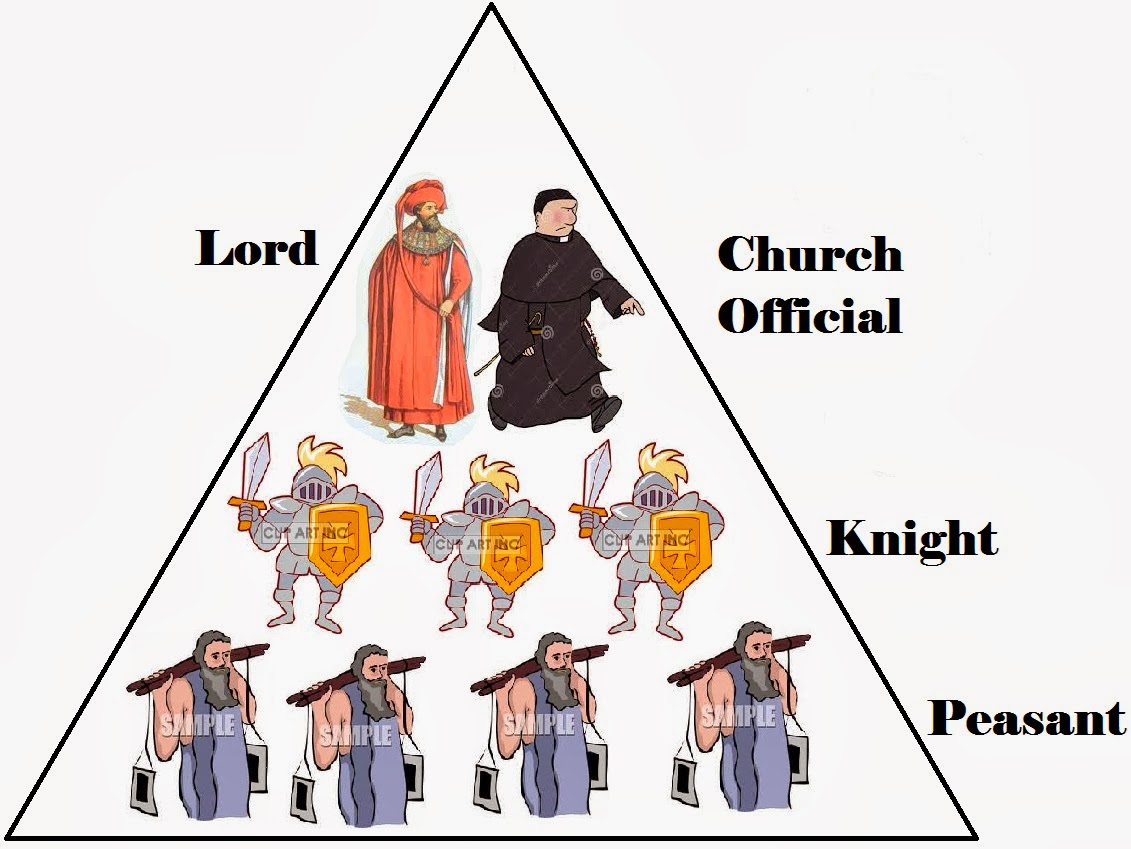
The training was far more holistic than just learning to fight in both Europe and Japan – warriors were expected to adhere to a code of honor at all times, and to act as aspirational role models to citizens. In both systems, warriors began their training at a young age. Knights and samurai were both considered their own separate class – above-average citizens, but below the nobility. Some aspects of feudalism can be witnessed even today in this country.Europe had knights, Japan had the samurai, but both valued military highly during their respective feudal periods. In the Japanese feudal system also, the distribution of people in various classes resulted in the diversification of people in the country.

This was a close description of feudal hierarchy of Japan which seized its existence in the 19 th century as the floating world came to an end. But as the time passed the merchants managed to grow their economic power and it resulted in weakening of the restrictions against them.

The Japanese theories even referred merchants as parasites as they were considered to be making profits from the labor & work done by the more productive class of peasants. The traveling traders and the shopkeepers constituted the lowest class in the Japanese feudal hierarchy. Some of the artisans were also involved in making swords and Boatwright for samurais. These were the people who produced the goods of daily requirements like utensils, clothes etc. They were placed higher in the hierarchy and enjoyed more privileges than the merchants or the artisans. Since they were the producers of the food on which the whole population and all the classes depended, they were considered as an honorable class. On the japan social hierarchy ladder, after the samurais the next position was acquired by farmers. Daimyos were the powerful warriors, also known as warlords, hence they were not made a part of this class system. But these classes were among the emperors and were the highest ranked people. There were people above samurais also for whom samurai worked, and Shoguns were the masters of Daimyos. The Japanese feudal system also forced lower class people to bow down in order to show respect while surpassing any samurai. If we look at the population of Japan, the samurai warriors constituted only 10% of the total population, but since they showcased enormous power along with their daimyos lords, they were placed on top. This was the topmost class of the feudal Japan which constituted of samurai warriors.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
